- UID
- 20
- Online time
- Hours
- Posts
- Reg time
- 24-8-2017
- Last login
- 1-1-1970
|
|
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
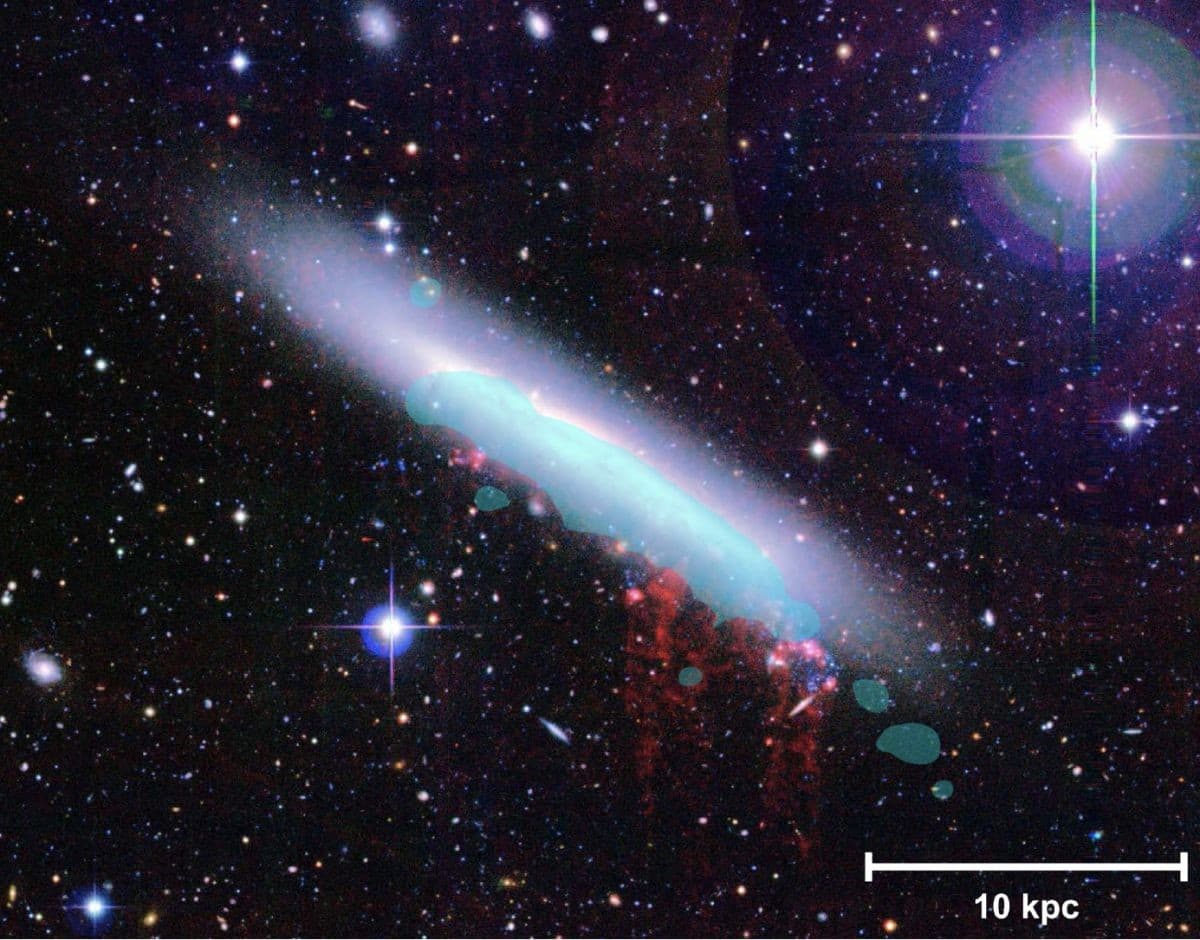
The spiral galaxy NGC 4330 is located in the Virgo Cluster. Ram-pressure stripped hot gas is shown in red, and a blue overlay shows star-forming gas.(Image: © Fossatie et al. (2018), Author provided)
▼ In the most extreme regions of the universe, galaxies are being killed. Their star formation is being shut down and astronomers want to know why.
The first ever Canadian-led large project on one of the world's leading telescopes is hoping to do just that. The new program, called the Virgo Environment Traced in Carbon Monoxide survey (VERTICO), is investigating, in brilliant detail, how galaxies are killed by their environment.
As VERTICO's principal investigator, I lead a team of 30 experts that are using the Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA)to map the molecular hydrogen gas, the fuel from which new stars are made, at high resolution across 51 galaxies in our nearest galaxy cluster, called the Virgo Cluster.
Commissioned in 2013 at a cost of US$1.4 billion, ALMA is an array of connected radio dishes at an altitude of 5,000 metres in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile. It is an international partnership between Europe, the United States, Canada, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan and Chile. The largest ground-based astronomical project in existence, ALMA is the most advanced millimetre wavelength telescope ever built and ideal for studying the clouds of dense cold gas from which new stars form, which cannot be seen using visible light.
Large ALMA research programs such as VERTICO are designed to address strategic scientific issues that will lead to a major advance or breakthrough in the field.
Galaxy clusters
Where galaxies live in the universe and how they interact with (▪ ▪ ▪)
► Please, continue reading this article here: Source |
|